Intervertebral disc herniation is more common in age-related osteochondrosis due to dryness and fragility of the fibrous ring. But this is only one of the risk factors. Others include:
- Heavy strain on the lumbar region due to overweight.
- Weakness of the muscular system.
- Heredity.
- Sedentary lifestyle and as a result of this constant compression of the spinal structures.
- Smoking.
- Great physical activity.
According to medical statistics, this disease occurs in men many times more often than in women.
What are the most common causes of the disease:
- Injuries from road accidents or falls.
- Lifting heavy objects with incorrect load distribution.
- Scoliosis or lordosis, leading to increased stress on certain areas of the spine.
- Hip dysplasia.
- Chronic diseases, including tuberculosis of the spine, neoplasms, syphilis.
- Metabolic disorders (hereditary and acquired).
All these factors cause wear and tear of the cartilage and bones of the spine. And this is the main cause of intervertebral hernia.
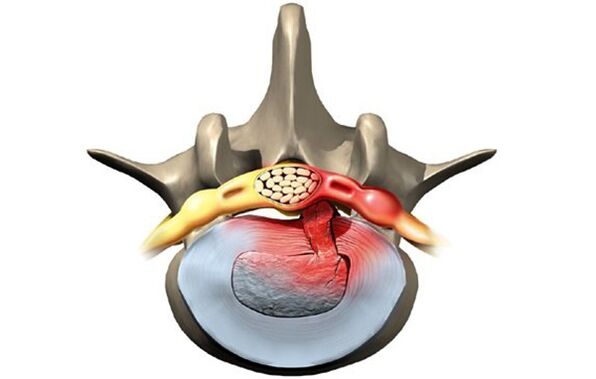
Stages of disease development
Without proper treatment, the disease progresses and the condition of the damaged spinal discs worsens. There are four stages in the development of the disease:
- Prolapse. The intervertebral disc has shifted considerably, no more than two millimeters. The pulpal nucleus does not extend beyond the body of the spine.
- Lumbar protrusion. The edge of the disc extends beyond the body of the spine to a distance of 1. 5 mm, but no displacement of the nucleus is observed.
- Extrusion. The nucleus extends beyond the vertebral body.
- Sequestration. The nucleus practically falls and hangs over the vertebra in the form of a drop. At this stage, there is a risk of rupture of the fibrous ring and leakage of fluid secretions.
In the first stage of the disease a person worries almost nothing, sometimes there is back pain, but they pass quickly. As the disease progresses, health also deteriorates, and symptoms become more painful and anxious. If the diagnosis is not made in time and treatment is not started, the consequences are possible: paralysis of the legs and serious disorders of the nervous system.
How does a lumbosacral hernia manifest itself?
An intervertebral hernia can present with the following symptoms:
- Lumbar pain.
- Pain when walking, radiating to the thighs.
- Numbness of the feet, toes, areas on the surface of the lower leg and thigh.
- Feeling of heaviness in the legs.
- Stiffness of movement.
In order not to be late in seeking medical help, it is worth analyzing the symptoms of the disease more carefully. They can be divided into three groups.
Pain syndrome
Pain with lumbosacral spine hernia is a key symptom. In the first stage there is pain in the damaged disc, especially after injury. They can increase or decrease and then reappear. More often, the sacral area does not even hurt, but hurts, especially during exercise or prolonged sedentary work. If a person lies on his healthy side and bends his legs, the pain completely disappears. This condition can last for several months.
With timely medical treatment, getting rid of the problem is easy. It is enough to say goodbye to bad habits and do the physiotherapy exercises recommended by your doctor.
Every day the affected area will increase and the condition of the disc tissues will worsen. The transition to the second degree of the disease is signaled by increased pain. It is now felt not only in the sacral area, but covers the entire lower back, radiating to the cervical area, to each spinal muscle, buttocks, thighs, legs, feet and toes. Discomfort manifests itself in physical activity, even minor - coughing or sneezing.
Vertebral syndrome
The increased pain in the second stage is accompanied by constant spasms of the back muscles. This leads to even greater discomfort for the patient. He cannot move freely, straighten his back, stretch. The gait of such a person becomes uncertain, he always leans to the side opposite to the patient, bends over.
Due to impaired coordination of movements, the quality of human life is deteriorating. He cannot perform well-assigned tasks and active rest becomes unrealistic due to constant pain.
Radicular syndrome
If the hernia is left unattended by doctors, the progressive disease leads to compression of the spinal roots, as a result of which they die, and access of blood to the tissues of the damaged disc is almost impossible. Symptoms characteristic of the severe stages of the disease appear:
- Weakening of the leg muscles. The patient cannot squat, stretch, jump. Even climbing stairs is difficult for him.
- Numbness in the affected area and surrounding areas. The skin becomes insensitive and pale, there is a feeling of tingling and numbness. Patients complain of hyperhidrosis in the affected area and legs or, conversely, excessive dryness of the skin.
- Lumbago. The patient suffers from lumbago in the lumbar region with sharp, sharp pain that intensifies with each movement. If left untreated, it leads to destruction of the hip and knee joints.
- Noticeable thinning of the inflamed leg, which leads to asymmetry of the posture.
- Pelvic disorders. Urological and gynecological diseases worsen, libido disappears, diarrhea and urinary incontinence are possible.
In severe cases of spinal hernia, there is a risk of paralysis, disability and even death.
Diagnosis of pathology
If a person has severe low back pain, he should make an appointment with a neurologist. He will conduct an examination with medical examinations:
- Identification of reflexes from the tendons of the lower extremities.
- Testing to lift the legs.
- Determination of sensitivity to heat or cold, pain and vibration on the entire surface of the legs, thighs, buttocks, abdomen and back.
The doctor will then refer the patient for an MRI or CT scan of the lumbar spine. With the help of tomographic techniques, a three-dimensional picture of the affected area will be obtained. It can be used to determine the location and size of the hernia, the stage of the disease.
Electromyography, neurography and contrast myelography are additionally prescribed at risk of spinal cord injury. With the help of these tests, the doctor will determine if emergency surgery is needed.
Treatment of disc herniation
Spinal hernias are treated both conservatively and surgically. The choice of technique depends on the stage of development of the disease, the presence of concomitant diseases and contraindications.
Conservative therapy
The therapeutic course is aimed primarily at relieving pain and relieving the patient's condition.
What pharmaceuticals can a doctor prescribe:
- Medicines that relieve pain and inflammation. In case of exacerbation - in the form of injections. Oral medications with a similar effect are prescribed to relieve acute pain (usually three to four days are sufficient).
- Blockade of novocaine with the addition of corticosteroids. Such a method is able to stop the pain for two weeks at a time. A course of blockades with injections in different parts of the damaged disc is usually performed.
- Centrally acting muscle relaxants. They reduce muscle activity by relieving pain cramps.
- Vitamin-mineral complexes with an emphasis on the elements of group B. They slightly relax the muscles, support tissue regeneration and the conduction of nerve impulses.
After relieving the pain syndrome, the intake of drugs decreases. The treatment of the disease is due to physiotherapy and physiotherapy.
Methods of physiotherapy are also chosen depending on the patient's condition. This can be:
- Heat or electric shock treatment.
- Electrophoresis with anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Acupuncture and acupressure.
- Hirudotherapy.
- Hydromassage.
Normal massage is permissible only if there is no pain syndrome. A more effective physiotherapeutic treatment is manual therapy with post-isometric relaxation.
Doctors strongly recommend that patients who smoke give up smoking.
Dietary adjustment is also important, especially for overweight patients. Fatty, salty foods, pastries and alcohol should be excluded from the menu. A fasting diet with plenty of vegetables and fermented dairy products will help the body better withstand the treatment, as well as get rid of the weight that weighs on the back.
Surgical intervention
Conservative treatment usually lasts about two months. If it does not give the desired result, a decision is made to change the therapeutic tactics or surgery. The latter is prescribed for severe pain, loss of sensitivity of the legs, pelvic dysfunction. Depending on the complexity of the situation, the operation is performed in the following ways:
- Endoscopic method. Three microincisions are made in the affected area. One has a radiation camera attached to the monitor. Through the other two, the protrusion of the hernia is removed with the help of miniature tools.
- By the method of percutaneous discectomy. The damaged nucleus is removed by puncture in the spinal disc and replaced with an artificial substance.
- By laser reconstruction. It is performed in the form of punctures with the help of a special needle without tissue dissection. Laser radiation warms the disc structures and stimulates cell regeneration, as well as relieves pain.
In difficult cases, endoprosthesis of the spinal discs is possible - replacement of the damaged organ with an implant.
Rehabilitation will be needed after complex surgical interventions. The operated person will have to wear a corset and will not be able to sit for about three months. The further rehabilitation period includes the practice of therapeutic gymnastics and physiotherapy.
Preventive techniques
Like any other disease, herniated discs are easier to prevent than to treat. What you need to do to keep your spinal discs healthy:
- Accurately calculate the loads if your work is related to them or if you are a professional athlete.
- Proper body weight (its index should not exceed 30).
- Choose a good mattress to sleep in the right position (preferably on your back).
- Engage in gentle physical education, swimming, fitness.
- Include exercises in the morning gymnastics to strengthen the muscular corset of the spine.
- Quit smoking.
- Eat well.
If following these rules becomes a habit, then there is a risk of getting a herniated spine just as a result of an accident.
Herniated discs are dangerous with serious consequences, and the treatment of advanced cases is very long. To avoid surgery and complications, if you have painful sensations in the back, you should visit a neurologist.
Osteochondrosis
The term osteochondrosis itself comes from two words: osteo - bone and chondrue - cartilage. Simply put, this is cartilage ossification. Although this interpretation is fundamentally wrong. Some go even further in their delusions and are convinced that osteochondrosis is the deposition of salts in the joints. In addition, table salt is eaten in large quantities.
Pathogenesis
In fact, everything happens a little differently. And harder. And table salt, if it plays a role in the occurrence of osteochondrosis, is very indirect. Osteochondrosis is based on dystrophy and degeneration of articular cartilage. This is not an independent disease, but a pathological process that can be observed almost anywhere where there is connective cartilage tissue.
However, osteochondrosis predominantly affects the spine. Why so? The fact is that between the vertebrae there is a kind of separators - intervertebral (intervertebral) discs. The physiological role of these discs is to cushion and protect the vertebral bodies from premature wear due to mechanical stress. The disc consists of an inner fluid pulpal nucleus surrounded by a fibrous ring and an upper and lower end plate.
The disk undergoes a huge mechanical load, which leads to permanent damage to its structures at the cellular level. In humans, these processes are very pronounced - this is our payment for upright walking. To prevent the disc from being completely "erased", it must be constantly regenerated, that is, restored. It is the balance of damage-regeneration processes that determines the normal structure of the intervertebral disc. Another interesting detail is that the blood and nutrient supplyintervertebral discs are carried out not through blood vessels that have grown in childhood, but diffusely, from the bone tissue of the vertebral bodies. Again, the payment for the ability to walk on two limbs, not four.
Therefore, intervertebral discs are easily injured anatomically and physiologically. Every negative process in the body leads to an imbalance of damage-regeneration and to the development of dystrophy and degeneration in the discs. A structurally defective disk is no longer able to withstand the proper mechanical stress. With excessive pressure from the upper vertebrae, the discs move in different directions, usually laterally and posteriorly. This process is called a herniated disc.
The bone tissue of the vertebrae, which has lost its cartilage sheath, also undergoes mechanical wear. Due to constant trauma to the anterior marginal surface of the vertebral bodies, pathological bone growths - osteophytes - are formed. Spondylosis develops. Due to degeneration and displacement of the disc, the intervertebral spaces shrink, the spinal canal narrows, and the roots of the spinal nerves hit the so-called foraminal holes.
Reasons
The causes or etiological factors for osteochondrosis are different. They can be both local, ie caused by the pathology of the spine and general disorders at the body level. Any pathology leading to a violation of the structure of the spine or to metabolic disorders can be considered a cause of osteochondrosis. In this regard, there are:
- Changes in the configuration of the spine (scoliosis, pathological lordosis or kyphosis)
- Other defects of the musculoskeletal system - flat feet, narrow shoulder girdle, pelvic anomalies
- Damage to the spine
- Weak immunity
- Metabolic disorders - osteoporosis, obesity, diabetes, thyroid disease
- Diseases of the cardiovascular system - atherosclerosis, hypertension
- Digestive disorders leading to insufficient absorption of nutrients from the gastrointestinal tract
- Heredity.
It should be noted that the above pathological conditions do not necessarily lead to osteochondrosis. This requires constant exposure to certain predisposing factors - hypothermia, malnutrition, sedentary lifestyle or, conversely, excessive exercise.
Symptoms
Osteochondrosis itself is an asymptomatic process. At the same time, the signs of degeneration of the intervertebral discs are diverse. How so? The fact is that the clinical manifestations of osteochondrosis are based on its complications - disc herniation, spondylosis, sciatica, narrowing of the spinal canal.
In addition, the clinic is very variable depending on the predominant localization of the process in the cervical, thoracic or lumbosacral spine. The last part is most often affected, as the lower back takes on maximum physical activity. Signs of osteochondrosis of the lumbosacral region:
- Pain (lumbodia, lumbago, sciatica)
- Restriction of movement in the lower back and lower limbs (intermittent claudication)
- Sensitivity disorders of the paresthesia type are observed here - tingling, burning, crawling
- Pathological tension of the lumbar muscles
- In the absence of treatment, disorders of pelvic organs.
Cervical osteochondrosis is slightly less common than lumbosacral osteochondrosis. However, this pathology is also quite common. In addition to the typical signs of pain (cervicalgia), decreased sensitivity and movement in the upper extremities, cervical osteochondrosis due to impaired blood supply to the brain has its own characteristics. These characteristics are manifested:
- Insomnia
- Headache, dizziness
- Periodic nausea
- General weakness, rapid fatigue
- Fluctuations in blood pressure
- Sometimes a toothache
- Behavioral reactions in the form of tearfulness, irritability.
The thoracic region with osteochondrosis is affected relatively rarely. Patients in this case are people forced to sit in a fixed awkward position in the profession - students, pupils, programmers, office workers. The symptoms of osteochondrosis in this case will be as follows:
- Chest pain and paresthesia
- dyspnea
- Feeling of palpitations
- Restriction of movement in the chest.
Diagnosis
From all this it is clear that osteochondrosis is a disease of the chameleon. Due to the similarity of the signs it is easy to confuse it with cerebrovascular accident, hypertension, myocardial infarction, angina pectoris, neurotic disorders. Therefore, in order to make the correct diagnosis, a comprehensive diagnosis is needed to correctly determine the symptoms and treatment of osteochondrosis.
This diagnosis, in addition to the traditional questioning and clarification of patients' complaints, should include a medical examination and special examination methods. These methods include X-ray of the spine, ultrasound of internal organs. Recently, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging have been used successfully to diagnose osteochondrosis.
Treatment
Therapeutic tactics for osteochondrosis include the use of:
- Medicines
- Massage
- Physiotherapeutic procedures
- Physiotherapy (exercise therapy)
- Manual therapy
- Acupuncture.
The drug for osteochondrosis is aimed primarily at relieving pain and eliminating inflammatory processes in the nerve roots. NSAIDs are used for this purpose. In various combinations, these drugs are widely used in the form of ointments, injections, tablets for the treatment of osteochondrosis. It should be remembered that these drugs have a negative effect on the liver, stomach and intestines. Thus, they may exacerbate metabolic disorders in osteochondrosis. They relieve the pain of blockade with local anesthetics. It is true that the effect of these drugs is short-lived and in no way affects the course of osteochondrosis in general.
It is possible to improve metabolic processes at the local and body level with the help of drugs such as chondroprotectors, immunostimulants and vitamins with minerals. Chondroprotectors are used in tablets, ointments and ampoules. Among the tonics are used vitamins C, group B, in combination with minerals. In this regard, calcium preparations are most preferred. In fact, contrary to some misconceptions, the basis of osteochondrosis is not an excess, but simply a deficiency of calcium.
After successful relief of exacerbation, physiotherapy, massage and exercise therapy are indicated. Calcium electrophoresis, hydrocortisone phonophoresis, amplipulse, paraffin therapy are used as physical procedures. All these measures are aimed at eliminating pain and inflammation in nerve roots, ligaments and muscles. The massage for osteochondrosis is performed according to the generally accepted method. The massage area is chosen depending on the location of osteochondrosis. The expansion of the range of motion is achieved with the help of exercise therapy. In the beginning, in the exacerbation phase, there are practically no dynamic loads. The patient is constantly in optimal position. At this time it is desirable to wear immobilizers - lumbar corset, collar on the neck of the trench. As the exacerbation is removed, the volume and duration of movements during training therapy increase.
Recently, non-traditional methods of treatment have been developed in the treatment of osteochondrosis - acupuncture, manual therapy, osteopathy. Acupuncture is an effect on special biologically active points located along the spine, on the earlobes, on the hands and feet. Manual therapy restores the normal position of the vertebrae and intervertebral discs through the manual action of the hands of a specialist. And in the course of osteopathy the structural integrity of the musculoskeletal system is ensured with specific techniques. In the absence of the effect of conservative measures for the treatment of osteochondrosis, persistent pain, complications, surgery is indicated. The pathologically displaced disc is removed. Microdiscectomy is currently being performed for this purpose - endoscopic removal of a displaced disc.



































