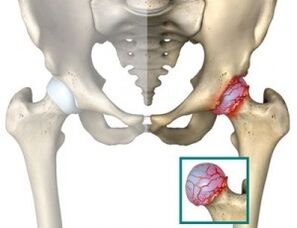
Coxarthrosis is a disease that affects the patient's hip joint. The treatment is long-term. Only a few decades ago, such a diagnosis was a practical sentence for a patient who promised him: severe debilitating pain, a gradual decrease in mobility, early disability.
But thanks to the most effective modern methods of treatment it became possible not only to stop the degenerative process, but even to completely cure coxarthrosis in the early stages.
Understanding the causes of the disease has led to the use of an integrated approach in therapy. Treatment of osteoarthritis of the hip may include both medication and physiotherapy.
What is hip osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is a disease in which the normal structure of the cartilage tissue of the joints is disrupted. Unlike arthritis, the cause of the deformity is not an infectious inflammation of the tissues, but a disorder in metabolic processes.
Deforming osteoarthritis of the hip, with rare exceptions, has been observed in patients over 40 years of age. The development of the pathology is as follows:
- Metabolism is impaired. Cartilage has no blood vessels, so it is nourished by the adjacent muscle tissue. The synthesis of substances is disturbed for various reasons.
- Due to insufficient nutrition, cartilage begins to lose its elasticity. Over time, it thins. The interosseous lumen is significantly reduced. Grade 3 osteoarthritis of the hip is characterized by the fact that the bone growths rub against each other. Cartilage is practically absent.
- The load on the bone, reducing the thickness of the cartilage, contributes to the deformation of the bone tissue.
After the onset of degenerative changes, it may take years for the patient to develop the third stage of the disease, but under adverse circumstances and failure to observe precautions, pathological changes can occur much more quickly.
How osteoarthritis manifests
The symptoms of osteoarthritis of the hip and their nature depends on the degree of development of the disease. The most common symptom is pain. It is because of the pain that patients most often turn to a doctor for qualified help. In addition, the insidiousness of the disease is that in the early stages of degenerative changes, pain usually does not cause great discomfort, is short-lived and is often due to ordinary fatigue.
The delay leads to the fact that the most appropriate time to start treatment is missed and the treatment of grade 2 hip osteoarthritis requires more time and effort. The chances of a successful prognosis still remain, provided the therapy is prescribed correctly.
The symptoms of the disease are:
- Pain - can occur in the thigh, groin and in the joint itself. It is worth being careful if the symptoms of pain appear at rest. This indicates the need for an urgent visit to an arthrologist.
- Stiffness of movements, lameness. It is observed after prolonged immobilization of the legs, for example after sleep.
- Over time, the diseased leg becomes shorter than the healthy one, there is atrophy of the muscle tissue, which is palpable.
Diagnosing a disease cannot be done without modern diagnostic tests. Thus, grade 1 hip osteoarthritis is diagnosed only with X-ray, CT and MRI. The picture clearly shows changes and narrowing of the interosseous lumen.
Stages of hip osteoarthritis
After diagnosing the pathology, the patient is assigned a code according to ICD 10. This is an international classification of diseases, which is reviewed every 10 years.
Thanks to the assigned code, not only statistics are collected. Therapies that have given the most tangible results can be selected. Thanks to international cooperation, the treatment of hip osteoarthritis has improved significantly over time.
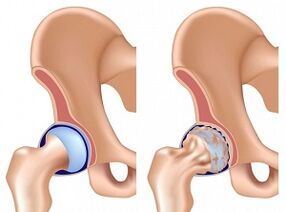
It is recognized in world practice that osteoarthritis of the hip joint has three stages or stages of development. Each of them has its own symptoms. Namely:
- First stage.Painful sensations occur only against the background of excessive load: running, exercise, exercise, etc. The pain is concentrated mainly in the joint area. Usually the pain disappears on its own after a short rest. At the same time, the mobility of the legs remains in full size, muscle strength is not limited. Osteoarthritis of the first degree can only be diagnosed with an X-ray or tomography. The image clearly shows small deformations of the bone tissue that do not go beyond the so-called articular lip. The joint space is slightly narrowed, usually in uneven areas.
- Second stage.It is characterized by migrating pain that begins to spread to the groin, thigh. It can occur spontaneously during rest. The pain in osteoarthritis of the hip in the second stage does not go away on its own and requires the patient to take anesthetics. The range of motion is disturbed and atrophy of the muscle tissue is observed. The image clearly shows bone growths and deformities of the femoral head. Perhaps the appearance of a cyst in the busiest part of the thigh - the acetabulum. Diagnosis of osteoarthritis in the second stage is performed quickly. Even on closer inspection, the pathological changes are obvious. X-rays or MRIs are done to see the extent of the deformity.
- Third stage.The pain begins to be chronic. It is possible to diagnose osteoarthritis even without a thorough examination. The patient cannot move without a cane, the pelvis is inclined, which leads to shortening of the legs. When moving, the patient should tilt his torso over the injured joint. As a result, it leads to even greater degenerative changes. The image shows extensive bone deformities. The joint space is almost invisible.
Therapeutic treatment of deforming arthrosis of the hip joint is effective only in 1-2 stages of the disease. The third stage of pathology often leads to the need for surgery.
How to treat osteoarthritis of the hip
Regardless of what is used, gymnastics for osteoarthritis of the hip or medication, all approaches are based on six basic principles. Namely:
- Eliminate the pain.
- Ensure normal nutrition of cartilage tissue and, if possible, restore it.
- Improve blood flow to the affected area.
- Reduce stress on the joint.
- Strengthen atrophied muscles.
- Restore joint mobility.
To achieve all six goals it is necessary to use complex therapy. For example, by prescribing injections into the joint, but without worrying about reducing the load on it, you can cancel all the beneficial effects of chondroprotectors. Not surprisingly, in world practice, 2 to 10 different approaches are usually used simultaneously, depending on the patient's condition.
How to treat hip osteoarthritis
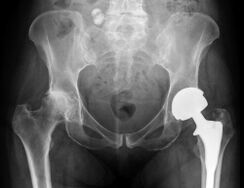
A comprehensive approach to the treatment of the hip joint provides better results than the use of only one therapeutic agent - a fact recognized by the world's leading arthrologists. Therefore, it is not uncommon for a patient to be prescribed several treatments at the same time:
- NSAIDs- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are a "classic" treatment. Medicines for osteoarthritis of the hip should be prescribed either in combination with non-steroidal drugs or in their composition. NSAIDs are especially effective during an exacerbation of the disease. They help relieve pain and reduce swelling. The reception gives the opportunity to perform exercises for exercises for osteoarthritis of the hip, to go for massage, gymnastics and other physiotherapy procedures. The disadvantage of NSAIDs is their negative effect on the gastric mucosa. Patients should understand that non-steroidal drugs for osteoarthritis do not cure the disease, but simply eliminate the symptoms, making treatment possible.
- Chondroprotectors and hyaluronic acid.These drugs are a new stage in the treatment of the hip joint, so they can be divided into a separate group.
- Chondroprotectors are prescribed as restorative therapy. With prolonged use, chondroprotectors repair damaged cartilage, but their effectiveness is limited by the initial stage of the disease.
- Hyaluronic acid builds a layer between the bones, allowing less strain on the joint. Effective as restorative therapy.
- Muscle relaxants- are vasodilators and can relieve muscle spasm. It is prescribed to reduce the load on the joint. Muscle relaxants can only be used as part of a complex drug therapy.
- Anesthetic Ointment- Despite advertisements for ointments as a miracle cure for the disease, they actually only eliminate the unpleasant symptoms of the disease. On the other hand, painkillers in the form of ointments increase the effectiveness of conservative treatment, allowing you to relieve puffiness and alleviate the patient's condition.
- Intra-articular injections- designed to relieve pain, restore cartilage or provide protection from excessive pressure on the joint. The most commonly used drugs are corticosteroids. They relieve pain by allowing the patient to begin treatment with physical therapy. The group of corticosteroids may also include preparations with hyaluronic acid. The effectiveness of intra-articular injections largely depends on how experienced the surgeon is (according to statistics, 30% of doctors miss the joint capsule when performing manipulations).
Some medicines can be harmful to the body. Self-medication is strictly forbidden!
Bandaging the hip joint will relieve stress on the joint and reduce the factor that is the main cause of tissue irritation leading to the inflammatory process. Therefore, along with drug therapy, fixation of the damaged area is often prescribed.
Alternative methods and physiotherapy
In addition to prescribing anti-inflammatory drugs, intra-articular injections and other drugs, the patient can undergo physiotherapy and use the help of non-traditional methods of therapy.
- Manual therapy- this procedure has a milder effect on the damaged tissues than the massage of the hip joint in osteoarthritis. Any aggressive effect on the affected area can easily provoke the onset of the inflammatory process. In our field, manual therapy is not yet accustomed, but in the West it is widespread and is one of the official methods of therapy.
- Physical therapyfor osteoarthritis deformity is an extensive area in which the patient can choose between traditional and non-traditional methods. Pilates, yoga, as well as water exercises and other ways to restore the function of atrophied muscles are popular in hip osteoarthritis. Physical education and moderate exercise, along with medication, have a beneficial effect and contribute to the patient's recovery.
- Traditional medicine- most arthrologists oppose this method as an independent therapy. And their opinion is justified. A large number of patients who refused the help of traditional medicine gained injuries. But under the supervision of the attending physician it is quite possible to effectively treat osteoarthritis of the hip with folk remedies. Most of the herbs and infusions used have anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects. Some medications have serious contraindications, so you should consult an arthrologist before taking them. It is recommended to use unconventional alternative methods for the treatment of osteoarthritis of the hip with caution. Some of the recipes not only do not contribute to improvement, but also lead to the opposite effect, provoking accelerated destruction of cartilage.
- Homeopathy- helps to normalize the synthesis of substances in the body. Homeopathy is especially effective in post-traumatic osteoarthritis, which allows you to deal with the main factor that led to the development of the disease.
- Apitherapy- treatment with bee stings is very effective, allows you to combine the effects of acupuncture and drug therapy. Not surprisingly, many warming and effective ointments contain processed bee venom. Apitherapy is often more effective than the hip bone. The appropriateness of the use of apitherapy should be decided by the attending physician.
- Magnetotherapy- used as an adjunct treatment and prevention of the disease. The effect of the magnet increases blood flow to the tissue, helps to restore metabolic processes. Removes salt deposits.
- Hirudotherapy- Leech therapy has been used for centuries. Leech saliva, which enters the bloodstream, has been shown to contain a substance that helps it liquefy. As a result, the blood may even enter atrophied capillaries and vessels.
- Mud treatment- has a gentle warming effect, helps to obtain the necessary nutrients. Proper application of mud therapy reduces inflammation and pain. Forbidden with purulent osteoarthritis of the hip joint. It is prescribed with caution in the presence of blood clots and vascular diseases.
- Shilajit for osteoarthritis- used both in pure form and as part of tinctures and compresses. The beneficial substances that make up Mumiyo promote tissue regeneration. Mummy is especially effective in the early stages of the disease.
- Self-massage- sharp aggressive cracks and pressure are excluded. During massage it is necessary to ensure the flow of blood and lymph. A chiropractor or an experienced masseur will show the types of movements and their direction.
Treatment of osteoarthritis of the hip at home with non-traditional methods should be supplemented with proper nutrition.
Losing only 5 kg will reduce the likelihood of an inflammatory process by about 30%.
Osteoarthritis of the hip and pregnancy
Pregnancy with osteoarthritis of the hip is a double stress for a woman's body. Most drugs are prohibited during pregnancy. At the very least, they should be taken with great care so as not to harm the baby.
If osteoarthritis of the hip during pregnancy is in the early stages, drug treatment is recommended to be postponed until after birth.
It is possible to be born with osteoarthritis of the hip, but it is necessary to understand all the risks involved. Complications after childbirth are not uncommon and deformation of cartilage tissue occurs at an increased rate.
Even during the planning of the child it is necessary to undergo a full examination of the body. All medicines, ointments, painkillers can be taken only according to the doctor's instructions.
Consequences of osteoarthritis
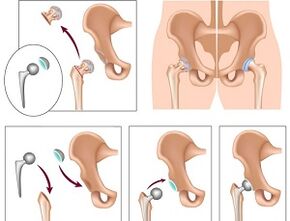
In the late stages of the disease, it becomes impossible to cure coxarthrosis in the usual way. Surgery required. The operation is a last resort and can be performed in different ways.
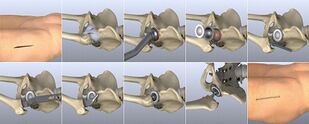
- Joint replacement- completely restores all motor functions. The disadvantage of this solution is the limited life of the prosthesis. On average, in 15 years, a second operation will be needed to replace it.
- Laser therapy for operated arthrosisof the hip joint - used in case of rejection of the articular bone. Using laser therapy, the damaged surface is removed and replaced with an artificial insert.
All types of operations are temporary, but without them the patient becomes disabled.
Early diagnosis of coxarthrosis and a properly prescribed course of rehabilitation therapy is the only reliable way to fight the disease. Ignoring the symptoms leads to damage.



































