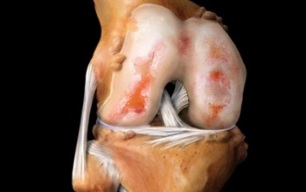
Gonarthrosis or arthrosis of the knee is a serious degenerative-dystrophic pathology of the knee joint, which causes destruction of the structure of the cartilaginous tissues of the joints, which in turn leads to their deformation and loss of their functions. The pathology often leads to human injuries.
Deforming gonarthrosis of the knee occupies a leading place among all arthrosis and if initially only a small part of the joint is affected, then in the absence of adequate treatment, when the disease progresses to a late stage of development, it all participates in the pathological process.
The disease most often develops in people over the age of 40, but in athletes it can occur at a young age (after receiving serious joint injuries).
Women are most susceptible to joint deformities, but this often happens in men and even young children. In order not to aggravate the situation, you should be able to recognize the first signs of this disease.
Varieties
The classification of gonarthrosis depends on its etiology and location. Each of the varieties has its own characteristics of development, which are always taken into account by the doctor when prescribing treatment. But by the nature of the manifestation they are practically identical.
Thus, the types of acute osteoarthritis of the knee joint, depending on the etiology of the disease, are as follows:
- Primary gonarthrosis.This disease develops without any preconditions. The risk group includes the elderly, women and obese patients. Primary type gonarthrosis of the knee joint can develop for years without manifesting itself in any way. But the sooner it is detected, the more favorable the prognosis for its treatment will be.
- Secondary gonarthrosisof the knee occurs due to trauma, but can also be a consequence of various infectious pathologies. If the damaged joints are treated in a timely manner, the patient has every chance to avoid this disease.
There are types of osteoarthritis by location:
- Right gonarthrosis, which develops in the joint tissues of the right knee. It is often found in athletes, as well as in people whose work requires frequent physical activity.
- Left gonarthrosisinvolves the left knee in the pathological process. It occurs in people who play sports professionally, as well as in patients diagnosed with obesity.
- Bilateral osteoarthritishas a destructive effect on the joint tissues of the knees of both legs. This type of disease is considered the most severe, both in terms of symptoms and in terms of therapeutic approach. In most cases, this type of gonarthrosis of the knee joint develops in the elderly, ie it is idiopathic.
Anatomy and pathological changes
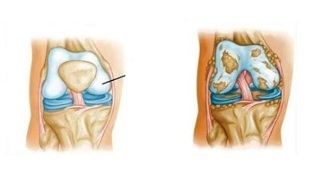
The knee joint is formed by the articular surfaces of the tibia and femur. In its front part there is a patella, which during movement slides smoothly along the recess located between the condyles of the femoral joint.
The femur and tibia together with the knee pad are covered with elastic clay cartilage, which is 5-6 mm thick. It helps reduce friction during physical activity by a person, and in case of falls, it performs a cushioning function.
Pathological changes in the joints: gradual disorders
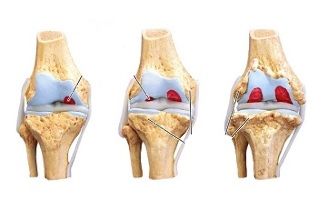
In the first stage of the development of gonarthrosis of the knee joint, in the first place, the blood circulation suffers. The small intraosseous vessels that supply blood to the hyaline joint are disrupted, leading to a gradual drying of its surface. It becomes less elastic and cracks begin to form on its surface.
As a result, instead of sliding smoothly, these cartilages touch each other. Inflammation gradually begins to develop and the diseased cartilage, slightly displaced, interferes with each other to fully perform its functions. Due to the formation of a large number of microcracks in the area of cartilage-building tissues, they gradually lose their cushioning properties.
In the second phase of gonarthrosis progression, compensatory changes in the bone area begin to occur. Under the influence of increased loads, the joint platform gradually begins to level, which leads to compaction of the subchondral area (the part of the bone that is located under the cartilage).
The joint surfaces at the edges begin to overgrow with bone processes that look like sharp thorns on an X-ray.
As the lubricating fluid in the joints thickens, it loses most of its function. This leads to accelerated cartilage degeneration. For this reason, it looks like a thin thread on an X-ray or becomes completely invisible.
If something like this is noticed, it means that the disease gradually (or quickly - it all depends on the situation) flows into the 3rd phase of development.
In the third stage of gonarthrosis of the knee joint there is a noticeable deformation of the bones. They seem to be pressed into each other, which reduces the mobility of the joints. The cartilage tissue dries almost completely.
Causes and predisposing factors

The causes of osteoarthritis of the knee are not isolated - often the doctor identifies several factors at once that led to the development of the disease.
The most common and common causes are:
- previous joint injuries (moderate or severe);
- leg fractures, especially if there has been intra-articular injury;
- violation of the integrity of the structure of the meniscus;
- ruptures or complete ruptures of connections;
- excessive stress on the knee joints.
Acute osteoarthritis of the knee is directly related to a person's age. Thus, it was found that people over 40 are most susceptible to it, because during this period the flexibility of cartilage begins to decrease and the lubricating fluid of the joints gradually "dries".
To delay this time, sports are recommended for patients, but physical activity should be moderate and not cause general discomfort.
Being overweight is also one of the factors predisposing to the development of gonarthrosis. The fact is that being overweight creates additional stress on the bones and joints, which can not but affect their health.
In this case, an important role is played by the fact which leg has more loads. For example, if your "support" is the left leg, then you are more likely to develop left-sided gonarthrosis.
In obesity, constant pressure on the joints leads to microtrauma and rupture of small blood vessels. Ruptures of the menisci or ligaments are also possible, which are considered a severe way to show joint injuries.
This disease is extremely difficult for patients with severe symptoms of varicose veins. In this case, the patient is shown a consultation with a phlebologist.
A high risk of developing this pathology also exists in people who:
- have previously suffered from various types of arthritis;
- have unfavorable heredity;
- have problems with the ligament apparatus;
- suffer from metabolic disorders;
- suffered a traumatic brain injury;
- were injured in an accident;
- had spinal injuries.
Many of these factors are often closely related. Accurately determining the cause helps to establish an accurate diagnosis and prescribe the correct and effective treatment for osteoarthritis of the patient's knee.
Clinical manifestations
The symptoms of gonarthrosis do not appear immediately - they begin to appear gradually, depending on the stage of the disease. For this reason, the clinical picture should be considered in stages.
First stage
In the initial stage of the disease, patients complain of mild pain in the knee, which increases with exercise. They become especially intense during the descent and ascent of the stairs.
In addition to the pain, the patient feels a certain stiffness of movements, "contraction" in the joint area. It is felt in the popliteal area and passes when the knee muscles are relaxed.
Another characteristic feature is the so-called "initial pain syndrome". It develops in the first steps of the patient. When the knees get used to the load, this anomaly disappears without a trace.
Second stage
At this time, the symptoms of osteoarthritis of the knee joint become more intense and noticeable. The pain intensifies, causing significant difficulty and discomfort when walking. The pain syndrome disappears after a long rest, but with intense effort it is felt again.
Inflammation of the joint causes swelling of the knee, which is visible even to the naked eye. There is a strong, unpleasant crisis when walking. The movements become heavier and more limited.
Third stage
The pain becomes very severe and the patient cannot do without painkillers. It is difficult for a person to bend the knee, he feels stiffness in the joints. It deforms and increases in size. In severe cases, the patient cannot move without additional support.
All these signs of osteoarthritis of the knee should not be ignored by the patient. The disease can put a person in a hospital bed for a long time and sometimes lead to injury.
Which doctor treats gonarthrosis of the knee?
For diagnosis and treatment of gonarthrosis of the knee it is necessary to visit an orthopedic traumatologist. If surgery is needed, you may need the help of a surgeon.
Diagnostic measures
In order to determine the cause of the disease, an integrated approach to the patient's examination is extremely important.
The diagnostic scheme consists of several stages:
- Visual examination of the orthopedist and taking a medical history. The doctor determines if the patient has symptoms of acute osteoarthritis of the knee, palpates the affected area of the leg, measures the bone and measures the angle - a test that can be used to assess joint mobility at different angles.
- Clinical blood test to assess ESR.
- Biochemistry of the blood.
- Examination of urine and blood for fibrinogen, urea and other substances.
- Radiography is one of the most common methods for examining osteoarthritis. In the initial stages, however, the snapshot does not show changes - they can be seen only in the later stages of development. The X-ray shows narrowing of the joint space, sclerotic changes in the cartilage area, bone damage and salt deposits.
- Ultrasound is the most informative diagnostic procedure. However, full results of the examination can be achieved if ultrasound is performed together with radiography.
- MRI allows you to thoroughly examine all layers of joint, cartilage and bone tissue and notice the first dystrophic changes in the early stages of osteoarthritis. However, MRI has one major drawback - the procedure is quite expensive. But its high accuracy contributes to 99, 9% accurate diagnosis.
Treatment
The treatment of acute osteoarthritis of the knee, as well as its diagnosis, requires an integrated approach. But in the first place it is necessary to apply drug therapy, as the diseased joint can become inflamed at any time.
Medicine
How to treat gonarthrosis of the knee joint with pharmaceutical drugs and which drugs to choose? Only a traumatologist will tell about it. Drugs from the following groups are often included in the treatment regimen:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs COX-1 or 2. The first group can seriously damage the gastrointestinal tract, so they can not be used for a long time. The same cannot be said for COX-2 drugs, which are more gentle. They are administered intramuscularly or intravenously.
- Treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee also includes the use of hormonal drugs. They help relieve inflammation and swelling in the knee. Their use is recommended if there is synovitis (inflammation of the synovial membrane).
- Treatment with chondroprotectors.
- Applying ointments, gels, creams. They improve blood circulation, warm up, relieve swelling and inflammation.
Method one
How is osteoarthritis of the knee treated with this technique? The main elements of the therapeutic scheme are:
- use of drugs (NSAIDs, chondroprotectors, painkillers, ointments, creams, gels);
- light physiotherapy exercises;
- manual therapy;
- physiotherapy;
- warming anti-inflammatory compresses with healing solutions.
In addition, according to a well-known rheumatologist, diet plays an important role in osteoarthritis. Thanks to a properly developed diet and the use of all the above techniques, you can achieve amazing results from therapy in the shortest possible time.
Method two
Often the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee, as well as other joint pathologies, is performed using this method.
The development of a renowned physician is based on the application:
- medicines;
- surgery;
- adherence to a diet that removes excess fluid from the body;
- kinesitherapy;
- physiotherapy.
The doctor also recommends more swimming in the pool, a visit to the sauna and a massage. This will help to improve the patient's health, especially if the disease has been neglected for a long time and has not been treated.
Treatment by the third method
The treatment of gonarthrosis of the knee joint with the help of this technique completely eliminates the dynamic loads, as they can significantly accelerate the process of deformation. The exercise should be slow, with low amplitude.
Example: sit on a chair "above", ie facing back. Spread your legs wide, but do not allow them to touch the floor. Gently swing each leg in turn. Do the exercise until you feel a little tired. The number of approaches depends on the patient's well-being.
Surgery
How to treat advanced osteoarthritis of the knee joints? In this case, there is only one way out - surgery. There are several types of surgery for osteoarthritis of the knee:
- Removal of deformed cartilage and diseased joint (arthrodesis). This is extremely rare.
- Removal of damaged cartilage tissue without removal of the joint. This intervention is called arthroscopic removal. It is performed with the help of a special device - an arthroscope. The procedure is simple, but the effect lasts no more than 3 years.
- Sawing and fixing the diseased joint from a different angle. This is called a periarticular osteotomy. The technique is quite complicated, but allows you to forget about the pathology for 3-5 years.
Surgery is rarely used and only in the absence of a method that cures the disease, at least for 1-2 years. In the early stages of the disease, surgery is almost never performed.
Endoprosthesis
Endoprosthesis is considered to be the most common treatment for gonarthrosis. This is a type of surgery that allows you to fully maintain the mobility of the affected knee. But despite its effectiveness, this technique requires long-term rehabilitation. Moreover, this can lead to quite serious consequences.
The place of the "real" patient is implanted with an artificial joint that can serve for 20 years. Although, of course, it all depends on the material from which it is made. The procedure is not cheap, but it is quite effective, which is why it has gained special popularity.
Physiotherapy exercises
The course of exercise therapy is prescribed by the doctor depending on the stage of the disease. However, the principles of performing the exercises are the same for all cases:
- avoiding intense stress on the knee joint;
- abrupt and forced movements are prohibited;
- do not perform exercises that require a full load on the inflamed joint.
Exercises allowed:
- gently shake your legs while kneeling on a blanket spread on the floor;
- neat kneeling movements in the same position;
- in the same position, straighten your legs in sequence, trying not to tear your heels off the floor, and then bend them again, avoiding sudden movements.
These exercises, combined with medication and physical therapy, give excellent results.
Physiotherapy
All physiotherapy procedures are prescribed for gonarthrosis in remission. Among the most effective techniques should be noted:
- electrophoresis with drug solutions;
- magnetic therapy;
- ultrasound therapy;
- microwave processing; paraffin therapy; baths with radon or hydrogen sulfide;
- treatment with mud.
To prevent a recurrence of the disease, physiotherapy courses should be taken at least twice a year. This will help prolong the remission phase.
Massage

Knee massage is performed to improve blood circulation. It is performed along the lymph flow in the direction from the peripheral zone to the central zone. The popliteal fossa is not involved in this process.
Often, along with the massage, manual therapy sessions are held, aimed at gradually stretching the diseased joint. Such procedures stabilize the patient's condition, but can only be performed by a specialist.
Is gonarthrosis completely cured?
Is it possible to completely cure osteoarthritis of the knee joint? Perhaps no one, even the most experienced traumatologist, will be able to give an unambiguous answer to this question. It all depends on the severity of the disease. If you engage in therapy in the early stages of its development, you can stop further deformation of the joints.
However, if pathology is found in the last stages, then even surgery does not guarantee the complete disappearance of unpleasant symptoms. The operation helps to heal in just a few years, after which the disease can remind itself again.
Prevention
To prevent gonarthrosis it is necessary:
- avoid knee injuries;
- exercise constantly (squatting, running, lifting and lowering the legs);
- enrich your diet with foods high in vitamins;
- limit the use of salt, hot spices, fried, smoked, jam;
- maintaining normal physical shape;
- immediate medical attention if you get the slightest knee injury;
- prophylactic use of chondroprotectors after reaching the age of 35;
- daily water intake (2 liters).
By following these simple recommendations, you will reliably protect yourself from osteoarthritis of the knee, as well as other diseases that can reduce your quality of life for a long time.



































